NP137-Lead asset

Netrin-1, an embyronic cue reactivated in cancer settings to promote tumor plasticity
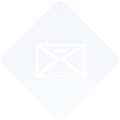
Netrin-1 is extensively known for its role during embryonic development (1). Netrin-1 has been described as a ligand for the prototypical dependence receptors DCC and UNC5B (2). DCC and UNC5B have been shown to have dual signaling depending on netrin-1 availability (3):
- in the presence of netrin-1, these receptors induce various intracellular signals including an Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) driving plasticity to cancer cells (Lengrand et al., Nature, 2023)
- in the absence of netrin-1, netrin-1 receptors induce cell death (Mehlen et al., Nat Rev Cancer, 2011 – Grandin et al., Cancer Cell, 2016)
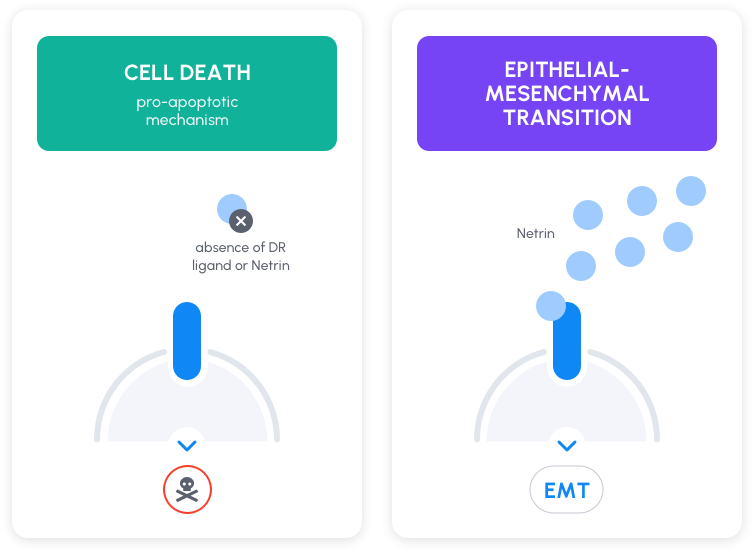
Netrin-1 is up-regulated in the vast majority of human cancer
Netrin-1, a protein normally only secreted during embryonic development, is gained in the vast majority of human cancer as a pro-tumoral mechanism.
Cancers in which netrin-1 is up-regulated are shown in the diagram. (see below the percentage of tumors overexpressing netrin-1 and references)
Netrin-1 titration is associated with tumor growth inhibition and plasticity
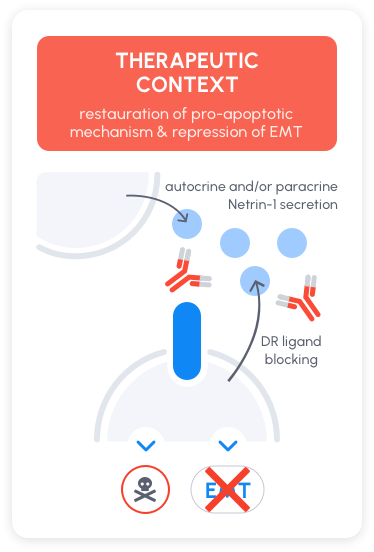
Experimental silencing or titration of netrin-1 is associated with tumor growth and EMT inhibitions. Upon interference to NETRIN-1, inhibition of EMT potentiates the anti-tumor activity of both chemotherapies and immune-checkpoint inhibitors.
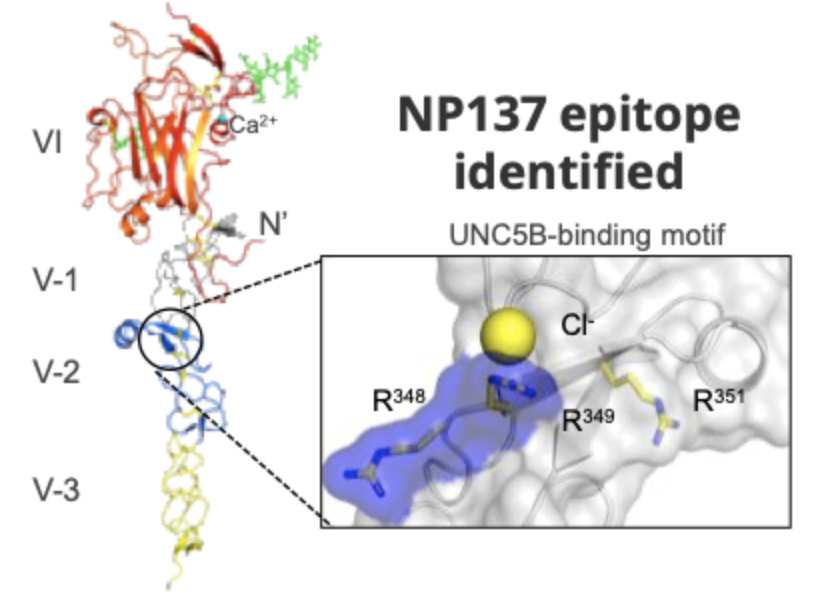
NP137 is a first-in-class, first-in-human, humanized monoclonal antibody of IGg1 isotype directed against netrin-1
NP137 was engineered to specifically and efficiently bind to netrin-1 and to inhibit the interaction ligand/receptor.
NP137 is alleviating resistance to chemotherapies and immunotherapies by modulating phenotypic plasticity
Because netrin-1 is both a survival factor and an inducer of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT), disrupting netrin-1 with NP137 is associated with both tumor growth inhibition and EMT inhibition. Because EMT is a natural break for the efficacy of chemotherapies and immune-checkpoint inhibitors, NP137 was shown in preclinical model to potentiate the anti-tumor activity of both chemotherapies and immune-checkpoint inhibitors.
NP137 is a safe product currently assessed in several phase II trials
NP137 confirmed its excellent safety profile during the clinical Phase I monotherapy, while presenting early signs of clinical activity with objective responses and disease stabilization. These signs of clinical activity, together with the confirmation of the reversion of tumoral EMT in patients treated with NP137, have led to conduct the ambitious GYNET phase 2 randomized trial assessing NP137 in combination with carbotaxol and/or pembrolizumab in patients with endometrial adenocarcinoma and cervix cancer. The clinical benefit of NP137 is also assessed in several other clinical trials in indications of strong medical interest as indicated below.